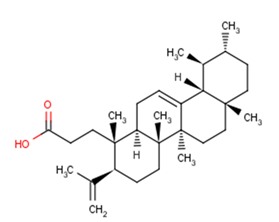
Roburic acid
CAS No. 6812-81-3
Roburic acid( —— )
Catalog No. M18992 CAS No. 6812-81-3
Roburic acid and phenethyl-trans-ferulate inhibit COX-1 and COX-2.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 87 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 170 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 295 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 444 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 620 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameRoburic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionRoburic acid and phenethyl-trans-ferulate inhibit COX-1 and COX-2.
-
DescriptionRoburic acid and phenethyl-trans-ferulate inhibit COX-1 and COX-2.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
RecptorCOX-1| COX-2
-
Research AreaInflammation/Immunology
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number6812-81-3
-
Formula Weight440.71
-
Molecular FormulaC30H48O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 33.33 mg/mL (75.63 mM)
-
SMILESC(=O)(CC[C@]1([C@@H](CC[C@]2([C@@]3(CC[C@]4(CC[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]4C3=CC[C@H]12)C)C)C)C)C)C(=C)C)C)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Cao H,et al. Discovery of cyclooxygenase inhibitors from medicinal plants used to treat inflammation. Pharmacol Res. 2010 Jun;61(6):519-24.
molnova catalog



related products
-
OV-1, sheep
This alpha-helical antimicrobial OV-1 ovispirin peptide derived from SMAP29 peptide.It was found to inhibit several antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains including mucoid and nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
-
Lasalocid
Lasalocid (Lasalocid-A) is an ion carrier antibiotic produced by Streptomyces, which has antimicrobial and parasitic properties and is often added to feed.
-
Garenoxacin mesylate...
A quinolone antibiotic for the treatment of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial infections.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


